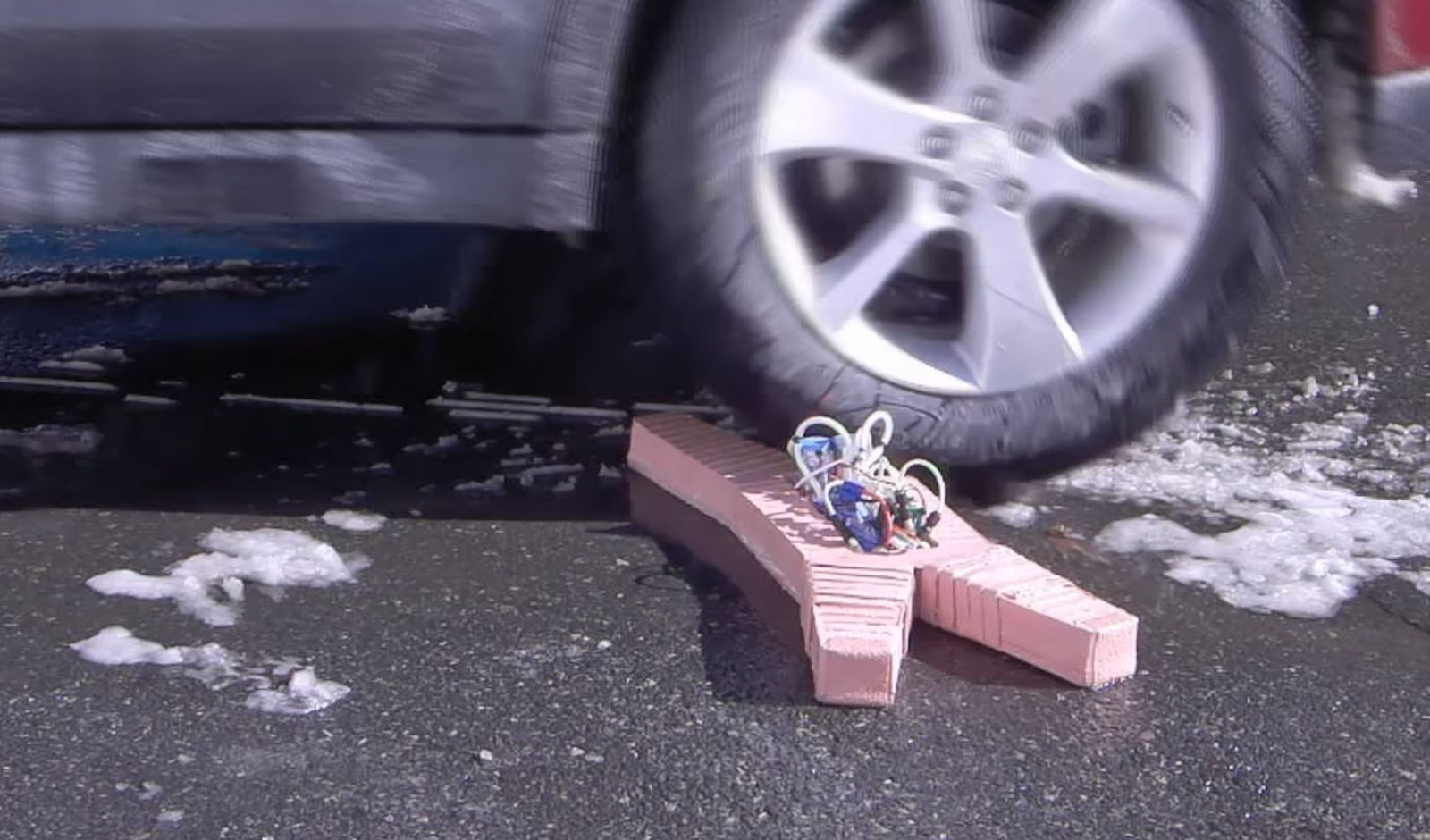
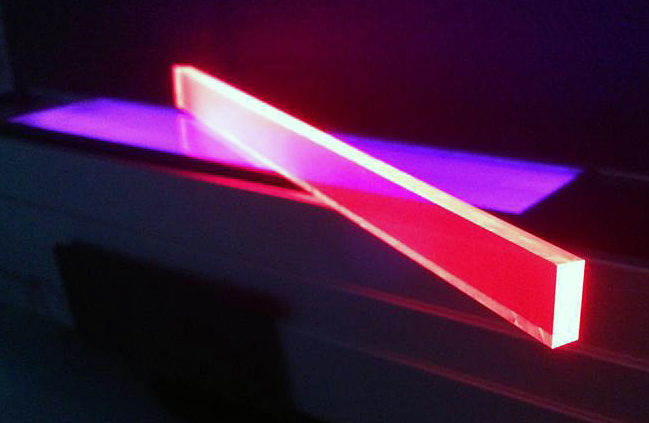
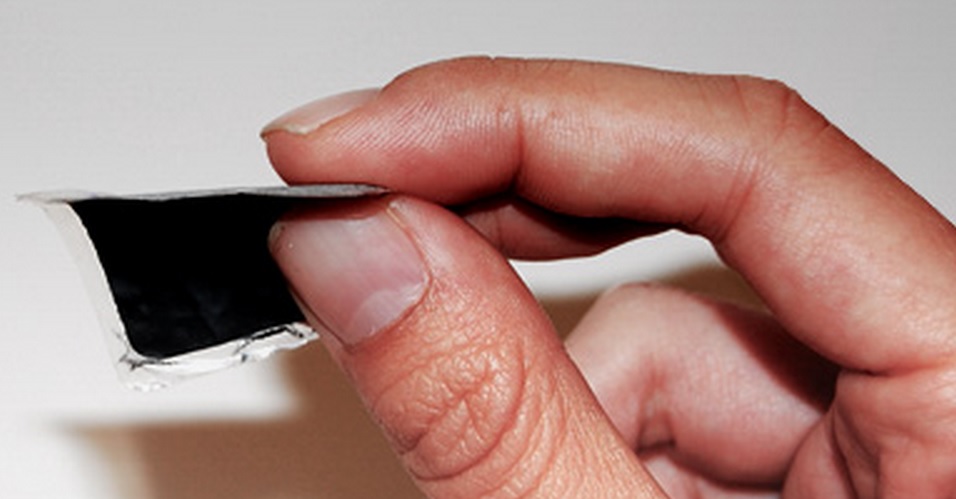
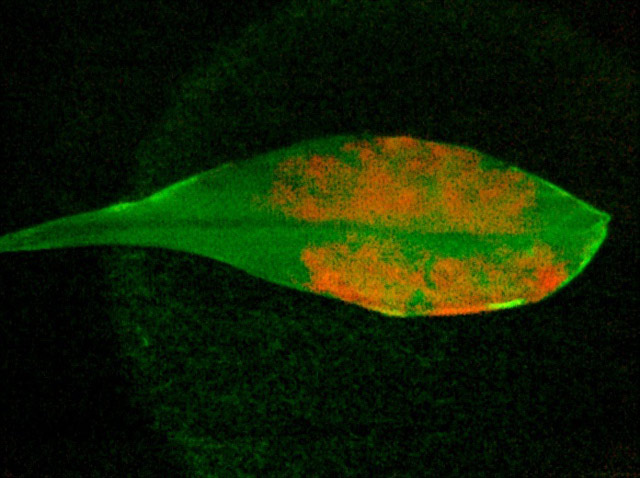
A London-based student developed a bio-reactive expiry label that decays at the same rate as food, potentially making a massive dent on the millions of tonnes of food wasted around the world each year.

The Bump Mark, which was the UK finalist of the James Dyson Award, uses a natural substance to tangibly show when a food product goes off.
"The Bump Mark contains gelatine - a protein - that reacts to environmental conditions, like temperature and light and anything that affects food," Solveiga Pakstaite, designer of the smart expiry label, told IBTimes UK. "Gelatine sets solid but it has the property that when it is fully expired it loses its structure."