The future of making things, from printable organs to intelligent clothes .
As the name suggests, additive manufacturing is the opposite of subtractive manufacturing. The latter is how manufacturing has traditionally been done: Layers are subtracted, or removed from a larger piece of material (wood, metal, stone, etcetera), leaving the desired shape. Additive manufacturing instead starts with loose material, either liquid or powder, and then builds it into a three-dimensional shape using a digital template, one layer at a time.
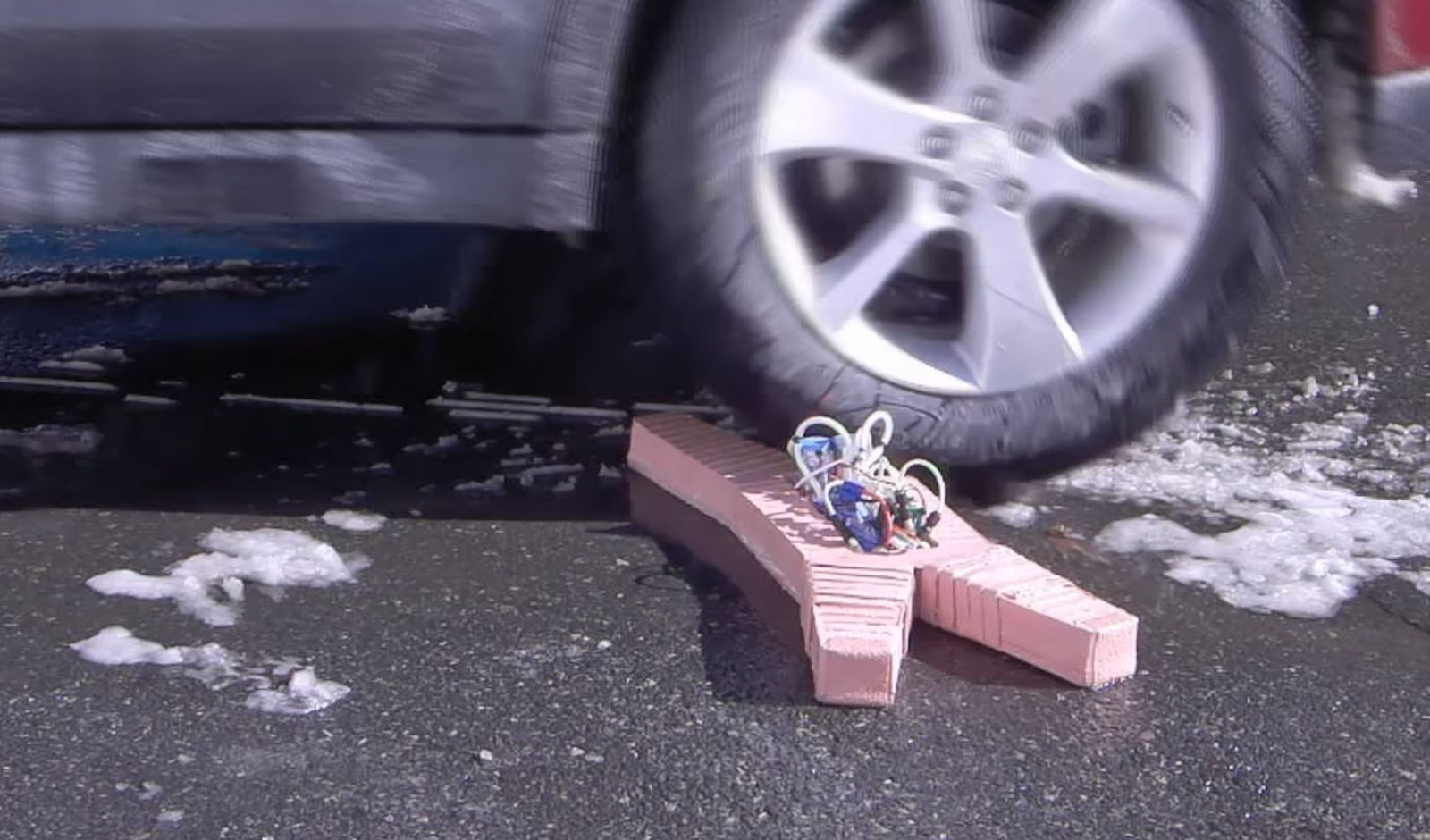
An important next stage in additive manufacturing would be the 3-D printing of integrated electronic components, such as circuit boards. Nanoscale computer parts, such as processors, are difficult to manufacture this way because of the challenges of combining electronic components with others made from multiple different materials. In other areas 4-D printing now promises to bring in a new generation of products that can alter themselves in response to environmental changes, such as heat and humidity. This could be useful in clothes or footwear, for example, as well as in health care products, such as implants designed to change in the human body.

Three-dimensional products can be highly customized to the end user, unlike mass-produced manufactured goods. An example is the company Invisalign, which uses computer imaging of customers’ teeth to make near-invisible braces tailored to their mouths. Other medical applications are taking 3-D printing in a more biological direction: Machines can directly print human cells, thereby creating living tissues that may find potential application in drug safety screening and, ultimately, tissue repair and regeneration.